This blog contains everything you need to know about HS including what it is, what the symptoms are, what causes Hidradenitis Suppurativa and the treatment options.
What is Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) is a chronic, inflammatory, debilitating skin disease that affects 1-4% of the general population. HS typically presents after puberty with painful, deep-seated lesions most commonly in areas of the body where skin rubs against the skin such as the underarm, under the breast, buttocks, thighs and groin. HS lesions can leak exudate which can sometimes have an unpleasant odour.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa Symptoms
The primary symptom of HS is a painful skin breakout that commonly occurs in the areas listed above. The breakout can include the appearance of red pimples, boils, deep nodules or cysts, and draining nodules. Over time these can develop into tunnels, scars and infections.
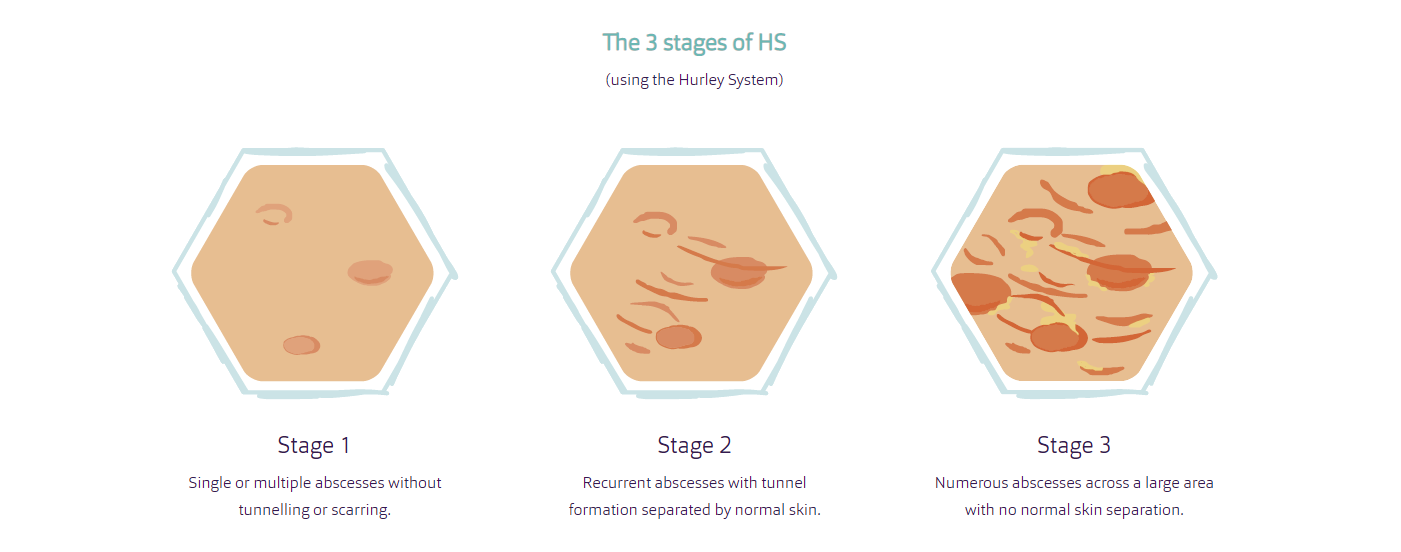
There are 3 stages of HS…
Factors that may worsen HS are:
- Stress
- Hormonal changes
- Heat
- Smoking
- Weight gain
What causes Hidradenitis Suppurativa
No one knows what causes Hidradenitis Suppurativa. What we do know is, it is not contagious and is not caused by poor hygiene.
Some studies show that many patients have a family history of HS and therefore it is believed to have a genetic element to it, but more research is needed.
As HS usually occurs after or during puberty when your body is going through a hormone change it is likely that hormones are involved in the development of the condition. But again, more research is needed in this area.
Risk Factors
Factors that may give you a higher risk of developing HS are:
- Being a woman (women are 3 times more likely to develop HS)
- Being overweight or obese
- Having a family history of HS
- Being between the ages of 20-29 years old, but not in all cases. HS can develop at all stages of life.
- Having severe acne, arthritis, Crohn’s disease, inflammatory bowel disease, metabolic syndrome or diabetes.
- Being a smoker.
Diagnosis
Receiving an early diagnosis is key to ensure you receive effective treatment that may help prevent you from progressing through the stages.
If you suspect you have HS, answer these two questions:
- Have you experienced a breakout of boils in the last 6 months?
- Where there more than one and located in multiple areas?
If you answered yes to both of those questions, then you may have HS and you should consult your doctor or dermatologist. A dermatologist is a doctor who specialises in skin disorders. If you do not have a dermatologist your doctor may be able to refer you to one.
Treatment
There is no cure for HS but there are some treatments that can help to relieve the symptoms. These treatments can lessen the pain, reduce the severity of breakouts, promote healing and prevent complications.
Your doctor may recommend any of the following treatments:
Acne washes or topical medications: These products may not necessarily help your symptoms if used alone but they can be helpful in addition to your other treatments.
Antibiotics: These can reduce inflammation, treat infections, and reduce the chance of new breakouts.
Bleach baths: Taking a bleach bath may help remove bacteria that colonise on your skin.
Biologics: Biologics work by suppressing the immune system. Biologics are often prescribed when other treatment options have failed.
Hormones: Some studies have shown hormone therapy may be as effective as antibiotics at treating sores but more research is needed in this area.
Metformin (Glucophage): This diabetes drug can also help people with HS who may also have metabolic syndrome.
Methotrexate: This is typically saved for treating severe cases of HS.
Pain medications: Over the counter pain killers such as paracetamol may help relieve discomfort caused by flare-ups.
Retinoids: These medicines come from vitamin A and can be taken orally or used topically.
Steroids: Oral or injected steroids can reduce inflammation and improve your symptoms, but long-term use is not recommended as it may lead to serious side effects.
Zinc: Some HS patients have noted improvements when they take zinc supplements.
Other procedures used to treat HS include laser therapy, radiation and unroofing. Wider surgical excision can also be an option.
Your treatment plan will depend on the stage of your HS. All HS patients react to treatments differently so you may have to try a few before you find something that works for you.
Complications
Untreated or severe cases of HS can cause complications such as:
Depression: HS can affect one’s confidence and self-esteem. Over time people may stop being as social as they once were, and this can cause depression to seep in.
Fistulas: The healing and scarring cycle of HS can cause hollow passages known as fistulas to form inside your body. These can be very painful and may need to be surgically removed.
Immobility: Painful breakouts, wounds and/or scars can limit your mobility.
Infection: There is a chance HS lesions and open wounds can become infected. It is very important to monitor your HS and know the signs of infection.
Lymph drainage problems: HS symptoms typically occur on areas of the body that are near lymph nodes. This can affect lymph drainage which may cause swelling.
Scarring: Scars can occur from having reoccurring breakouts in one area. Over time you can develop thick scars.
Skin cancer: In very rare cases, people with very advanced HS have also developed a type of skin cancer known as squamous cell carcinoma on the areas where they had breakouts and scarring. Do not be alarmed by this. The cases are very rare. But if you are concerned, talk to your doctor.
Skin changes: Areas of your skin may appear pitted or darker.
HidraWear Note
Living with HS can be challenging. If you would like to meet other people living with HS to chat about what they find works well and share your own tips and tricks you can join our HS Facebook community.